Rhybudd Tywydd
, 12 Rhagfyr 2014
Helo gyfeillion y gwanwyn!
Nadolig Llawen a diolch i bawb am anfon eich data ata i. Daliwch ati!
Rydyn ni’n adeiladu llun diddorol o’r gwahaniaeth yn y tywydd ar draws y wlad. Yr wythnos diwethaf cofnododd Ysgol Carnforth North Road yn Lloegr dymheredd isel o 3°C ac Ysgol Mossend yn Bellshill, yn yr Alban, dymheredd uchel o 13°C am yr un diwrnod! Dyna wahaniaeth! Os ydych chi wedi profi tywydd eithafol gallwch chi ddefnyddio’r map i gymharu cofnodion ysgolion eraill ar yr un diwrnod. Rhowch wybod os ydych chi’n darganfod rhywbeth diddorol.
Rwy’n edrych ymlaen yn fawr i weld eich cofnodion o’r wythnos ddiwethaf. Roedd Swyddfa Dywydd y DU wedi rhagweld tymheredd is ac eira mewn rhai mannau hyd yn oed. Os ydych chi wedi gweld eira, gofynnwch i’ch athro anfon ffotograff. Efallai y galla i ddangos rhai o’r lluniau ar y blog bylbiau.
Rhoddwyd rhybudd melyn am wynt, eira a iâ mewn rhai rhannau o’r DU. Mae rhybudd melyn yn golygu bod posibilrwydd o dywydd gwael yn yr ardal honno. Bydd y Swyddfa Dywydd yn ein rhybuddio am dywydd garw er mwyn i ni baratoi. Gall tywydd garw (fel gwynt cryf a iâ) achosi problemau a’i gwneud hi’n anodd teithio. Weithiau bydd ffyrdd, rheilffyrdd a hyd yn oed ysgolion yn cau oherwydd tywydd gwael.
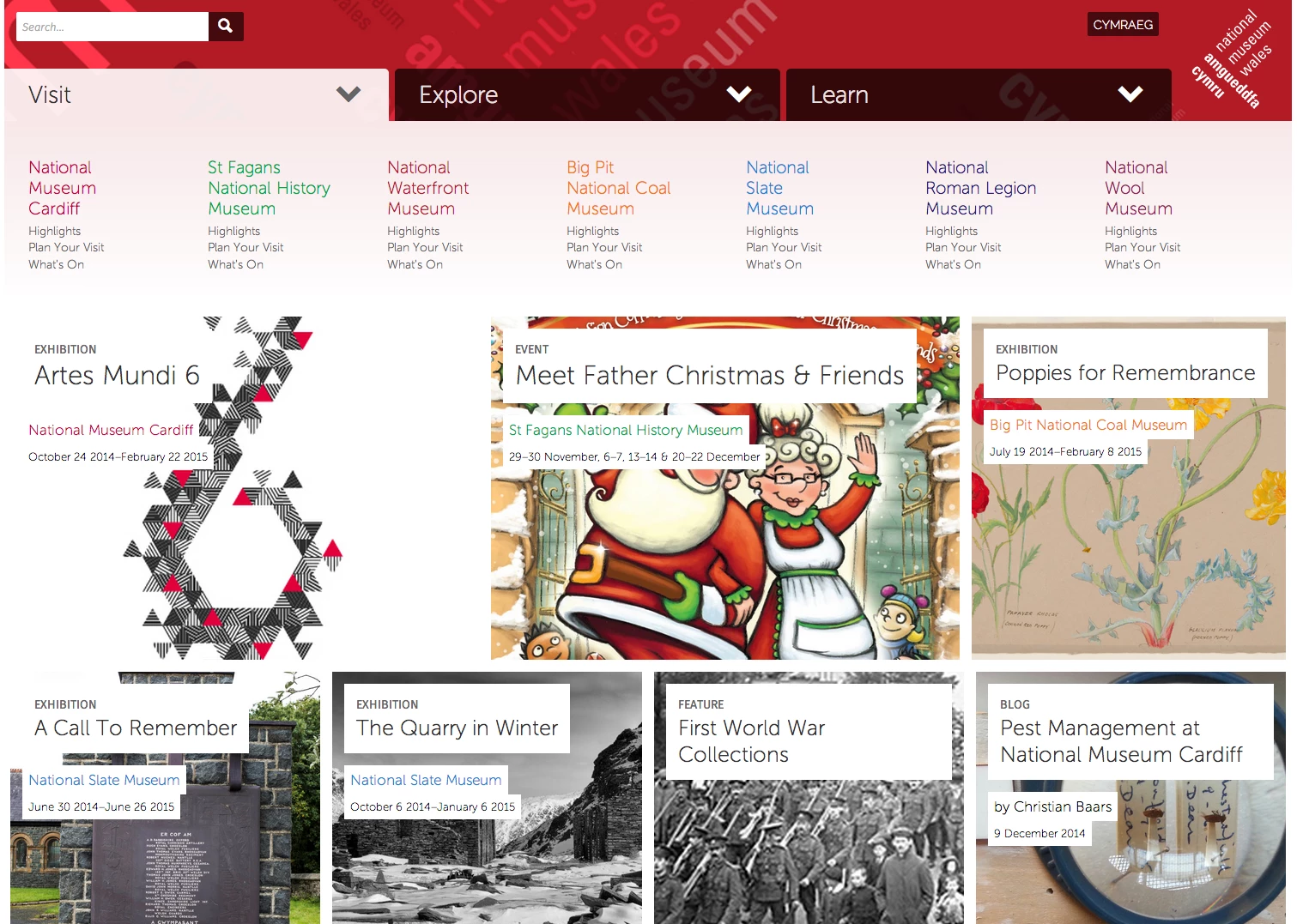
Mae’r siart lliw yma yn dangos y cod sy’n cael ei ddefnyddio i rybuddio pa mor arw yw’r tywydd.
Dim tywydd garw Gofalwch Paratowch Gweithredwch
Gwyrdd: dim tywydd garw
Melyn: posibilrwydd o dywydd eithafol, gofalwch
Ambr (oren): posibilrwydd cryf y bydd y tywydd yn effeithio arnoch chi mewn rhyw fodd, paratowch
Coch: disgwyl tywydd eithafol, ar ddiwrnod Rhybudd Coch efallai bydd eich rhieni chi’n gorfod cynllunio teithiau a gweld pa ffyrdd sydd wedi cau.
Mae’r Swyddfa Dywydd hefyd yn defnyddio symbolau i ddangos pa fath o dywydd i’w ddisgwyl. Dyma symbolau yn dangos rhybudd coch am law, rhybudd gwyrdd am wynt ac eira, rhybudd ambr am iâ a rhybudd gwyrdd am niwl. Bydd hin bwrw glaw yn drwm a dylech chi baratoi am iâ. Beth am edrych ar wefan y Swyddfa Dywydd ac edrych ar ragolygon y tywydd yn eich ardal chi?
Symbols to show what weather to expect (via the Met Office website).
Rydych chi’n gwneud gwaith gwych gyfeillion!
Athro’r Ardd
Eich cwestiynau, fy atebion:
Ysgol Gynradd Stanford yn y Vale – Llawer o law ar ddydd Llun ond braidd dim am weddill yr wythnos! Mae’r tywydd wedi dechrau oeri go iawn, yn enwedig ar ddydd Mercher ac roedd hi’n rhewi bore ‘ma (dydd Gwener) ac mae’r plant yn dal i obeithio am eira!!! Mae’r plant wedi cyfansoddi cân ar gyfer cofnodi’r tywydd a’r tymheredd – mae nhw’n gantorion gwyddonol. Athro’r Ardd – Helo gantorion gwyddonol, am enw gwych! Rydych chi’n swnio fel criw llawn sbort a dwi’n siŵr bydd canu yn helpu’r planhigion. Allech chi anfon geiriau’r caneuon ata i neu recordiad ohono chi’n canu? Dim chi oed yr unig ysgol i eld dydd Mercher oer, dyma Ysgol Rhys Prichard ac Ysgol Hiraddug yn nodi eu bod rhew yn drwm ar lawr ar ddydd Mercher.
Ysgol Gynradd Glyncollen – Mae un o’n bylbiau dirgel yn dechrau tyfu hefyd ac rydyn ni i gyd yn ceisio dyfalu pa flodyn yw e. Rydyn ni’n mwynhau’r project. Diolch Athro’r Ardd. Blwyddyn 4. Athro’r Ardd – Helo Blwyddyn 4, Rwy’n falch eich bod chi’n mwynhau’r project! Mae’n wych bod eich bylb dirgel chi’n dechrau tyfu hefyd, alwch chi anfon llun ata i? Gadewch i fi wybod pan fydd y blodyn yn agor, allwch chi ddyfalu beth yw e?
Ysgol Gynradd St. Ignatius – Mae llawer o’n planhigion ni wedi marw’n barod! Athro’r Ardd – Helo St. Ignatius, Mae’n ddrwg gen i eich bod chi’n cael trafferth gyda’r bylbiau. Bydda i’n cysylltu i gael mwy o wybodaeth. Os oes unrhyw ysgolion eraill yn cael problemau, cysylltwch â fi hefyd.