Enillwyr Bylbiau'r Gwanwyn i Ysgolion yn ymweld ag Amgueddfa Werin Cymru Sain Ffagan
, 10 Gorffennaf 2023
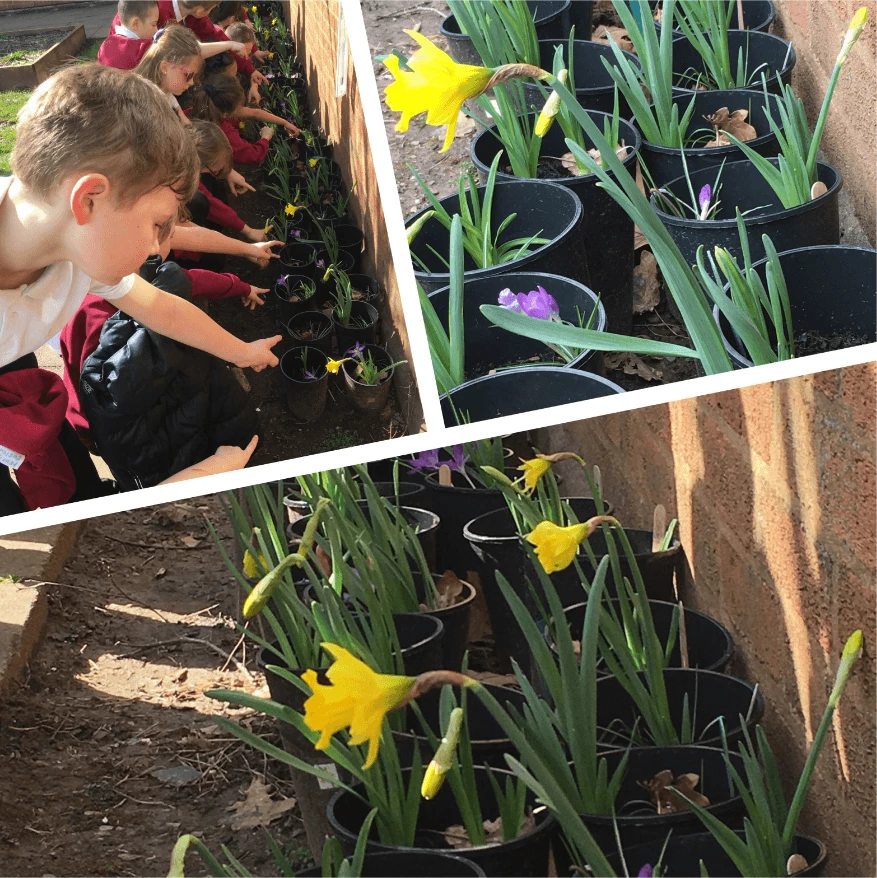
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model o Gaerfyrddin oedd enillwyr Cymru ar gyfer Ymchwiliad Bylbiau’r Gwanwyn i Ysgolion eleni. Gwnaeth yr ysgolion oedd yn cymryd rhan yn y project blannu eu bylbiau ym mis Hydref, cadw cofnodion tywydd rhwng Tachwedd a Mawrth, monitro eu planhigion a chofnodi dyddiadau blodeuo a thaldra'r planhigion, ac uwchlwytho'r holl ddata hwn i wefan Amgueddfa Cymru.
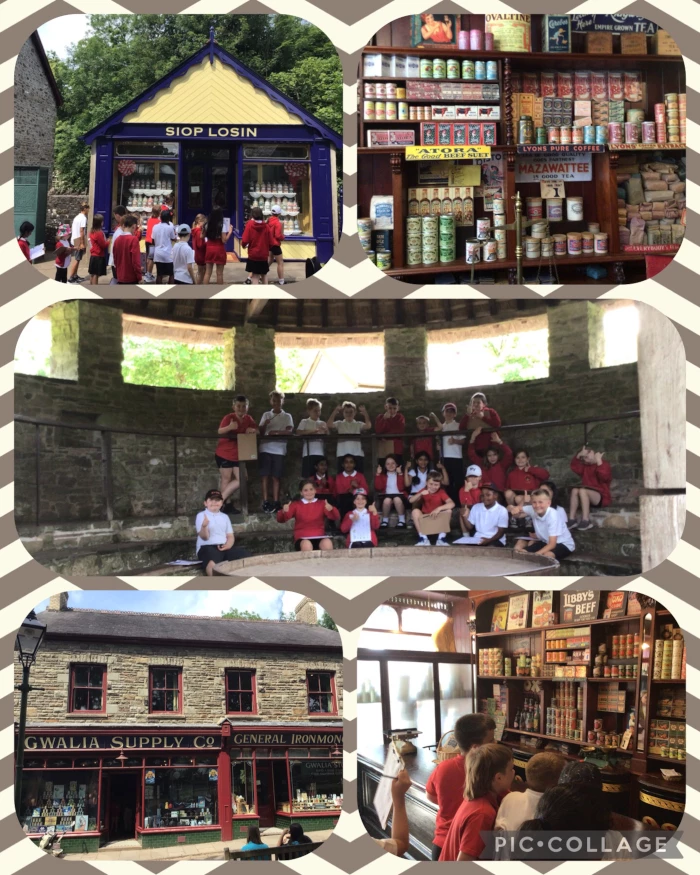
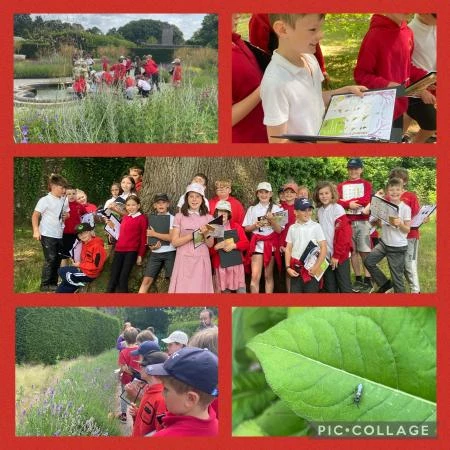
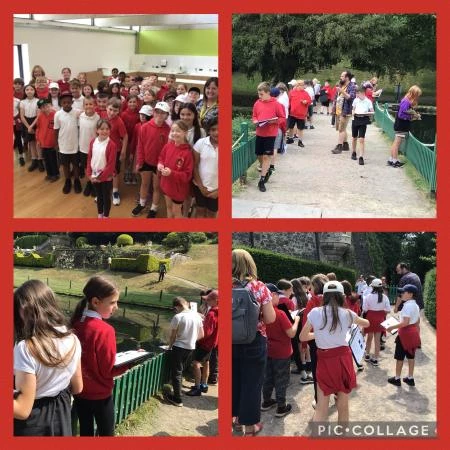
Y wobr ar gyfer yr ysgol sy'n ennill yng Nghymru bob blwyddyn yw trip i un o saith amgueddfa Amgueddfa Cymru, gyda bws am ddim a gweithgareddau. Eleni, dewisodd Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model ymweld â Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru. Roedd y diwrnod yn cynnwys Llwybr Cynaliadwyedd yn edrych ar rai o adeiladu hanesyddol yr amgueddfa a Helfa Drychfilod Feddylgar, lle buom yn chwilota yn rhai o erddi hardd yr amgueddfa.
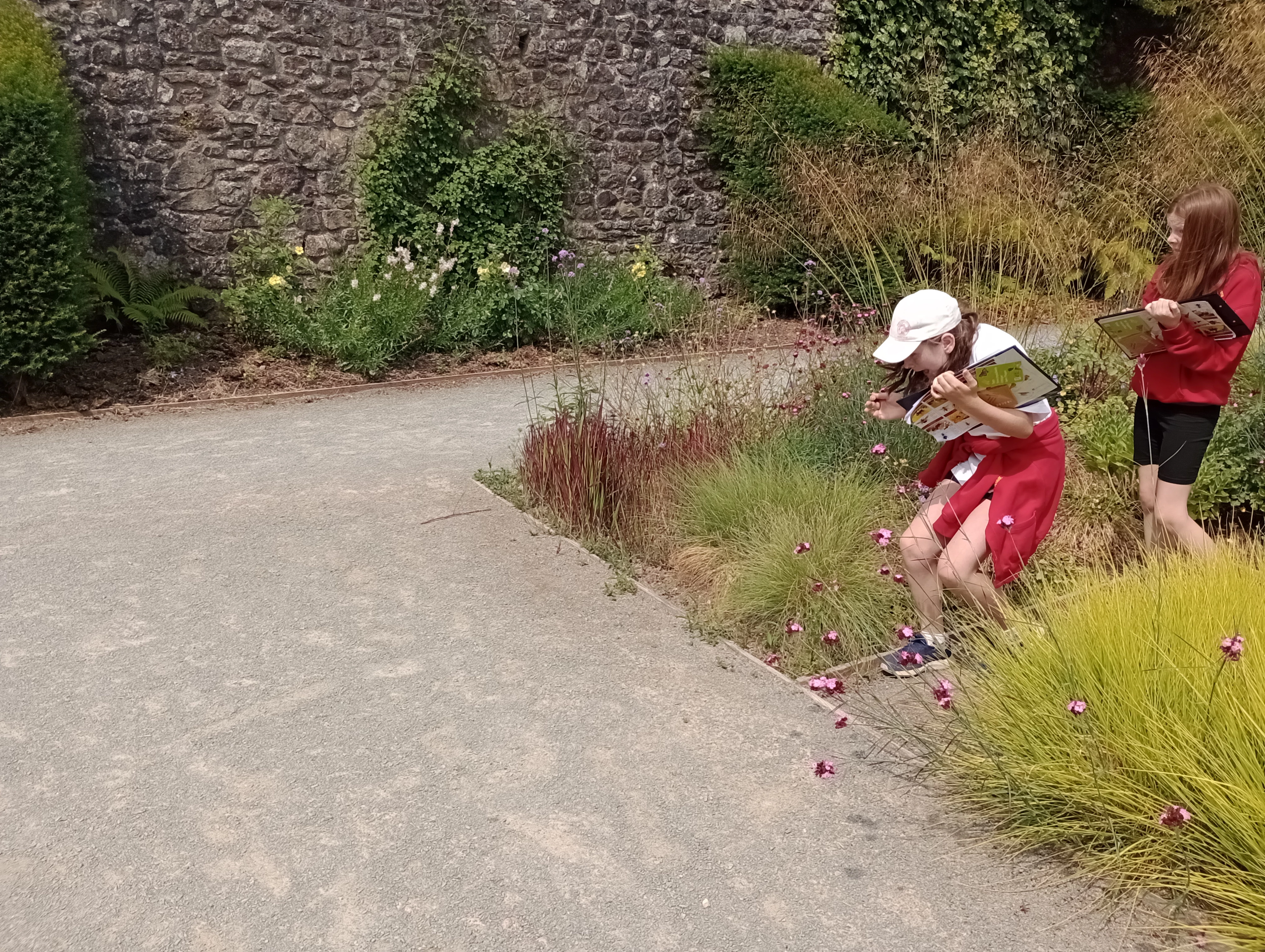
Roedden ni'n lwcus iawn ar ein Helfa Drychfilod Feddylgar, a oedd yn cynnwys bod yn ymwybodol o'r ardal o'n cwmpas ac edrych yn graff, gwrando'n astud ac arogli'n ddwfn. Gwelsom fursennod emrallt a saffir yn dawnsio uwchben y dŵr yn y pyllau pysgod, a llawer o bysgod bach yn nofio'n chwim o dan y dŵr. Roedd rhai yn ddigon ffodus i gael cip ar neidr y gwair wrth iddo lithro i'r dŵr ac i ffwrdd.
Gwelsom wenyn prysur a gloÿnnod byw lliwgar yn peillio planhigion ag aroglau pêr arnynt fel lafant. Gwelsom a chlywsom sioncod y gwair ym mhrysgwydd y gwelyau blodau, yn ogystal â buchod coch cwta, pryfed gleision, morgrug, chwilod, nadroedd cantroed, malwod, chwilod clust, a phryfed lludw. Roedd rhaid i ni blygu i osgoi gwas y neidr a oedd yn bwydo ar bryfed uwch ein pennau, yn plymio tuag atom sawl gwaith.
Buom yn gwylio a gwrando wrth i wenyn suo o amgylch twmpath yn y lawnt, gan dyrchu cartrefi newydd yn y pridd. Gwelsom gannoedd o bryfed cop ifanc yn byrstio allan o'u coden ac yn gwasgaru dros wrych.
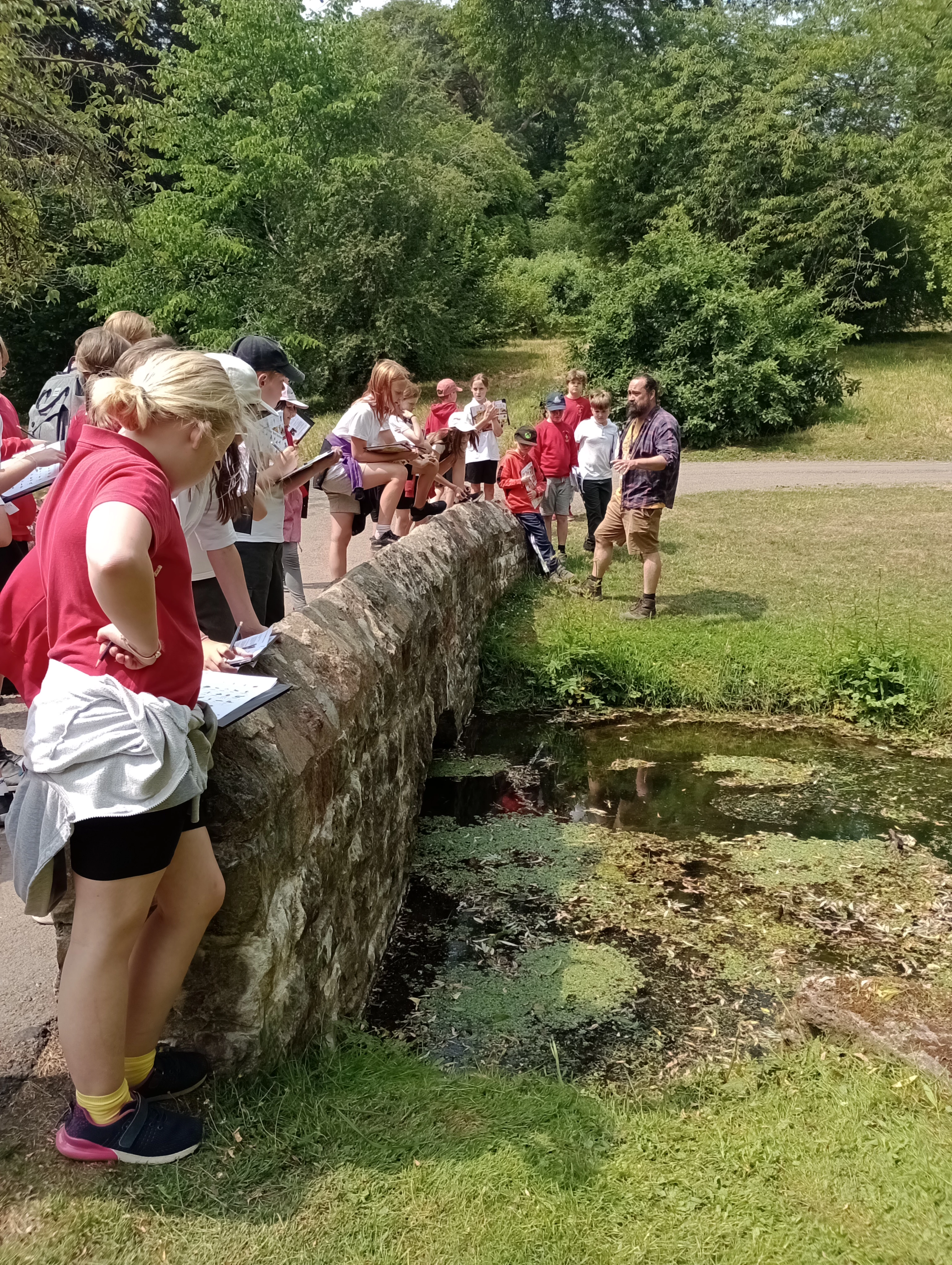
Gwylion ni gychwyr yn nofio'n hamddenol heibio'r bont garreg, a malwod dŵr oddi tani yn bwydo'n araf ar algâu. Gwylion ni'r hwyaid gwyllt cyfarwydd, gwyddau Canada urddasol a'u holl gywion ifanc wrth iddynt barhau â'u diwrnod ar hyd glan y dŵr.
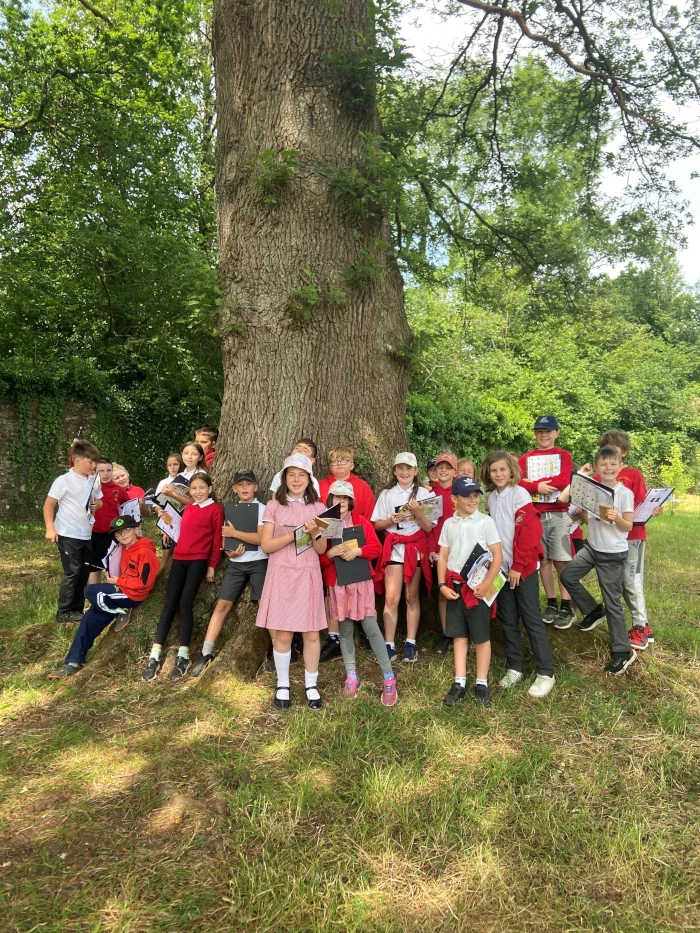
Gwnaethom adnabod gwahanol blanhigion a choed a gweld faint ohonom oedd ei angen i amgylchynu’r dderwen 400 oed. Roedden ni gyd wedi ymgolli'n llwyr yno.
Mae Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model wedi rhannu'r lluniau canlynol gyda ni i ddarlunio eu diwrnod yn yr amgueddfa.
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model yn Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model yn Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model yn Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model yn Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model yn Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model yn Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model yn Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru
Ysgol Wirfoddol Eglwysig y Model yn Sain Ffagan Amgueddfa Werin Cymru