Y canlyniadau hyd yn hyn: 2018-01-22
, 22 Ionawr 2018
Am dywydd diddorol Gyfeillion y Gwanwyn!
Wrth edrych trwy ein canlyniadau o 2011 i 2017 (gan ddefnyddio'r siart ar y dde), gallwn weld fod Tachwedd a Rhagfyr 2017 wedi cael tymheredd a glawiad llai na'r cyfartalog, ond oriau o haul uchaf na'r cyfartalog! Drwy gymharu'r data ar gyfer 2017 gyda blynyddoedd blaenorol, gallwn weld cafodd Tachwedd a Rhagfyr 2017 yr oriau o haul trydydd uchaf ers i ni gychwyn ein cofnodion.
Beth am weithio allan eich darlleniadau cyfartalog ar gyfer mis Tachwedd a Rhagfyr a chymharu heu’n hefo’r darlleniadau yn y tabl?
Mae nifer ohonoch wedi rhoi gwybod bod eich planhigion wedi cychwyn tyfu! Ydych chi'n meddwl y bydd y Crocws neu’r Cennin Pedr yn ymddangos yn gyntaf? Beth am edrych drwy’r adroddiad llynedd a chymharu'r dyddiau blodeuo ar gyfer y Crocws a’r Cennin Pedr i'ch helpu penderfynu pa un fydd yn tyfu’n gyntaf?
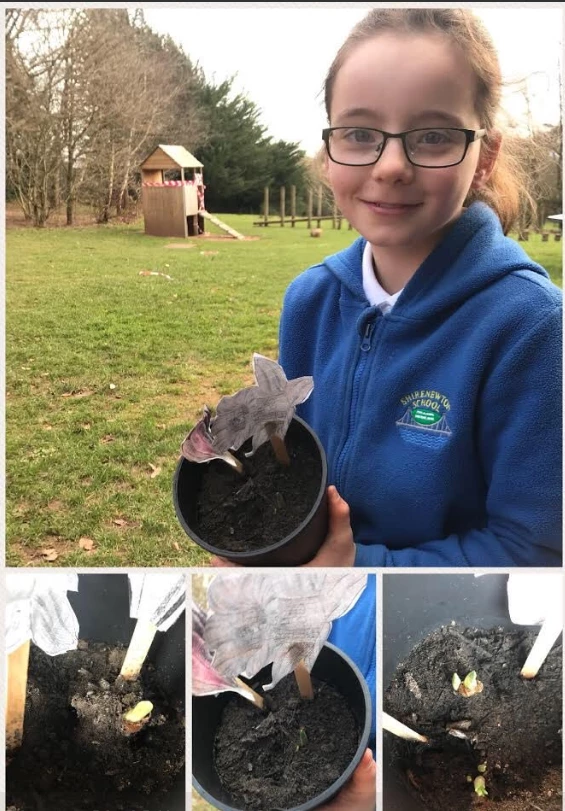
Rwyf wedi atodi lluniau gan ysgolion a rhannwyd ar Twitter. Plîs rhannwch eich lluniau fel bydda’n gallu dangos nhw ar fy blog nesaf!
Daliwch ati Gyfeillion y Gwanwyn,
Athro'r Ardd
Eich sylwadau:
Ferryside V.C.P School: Mae wedi bod yn wythnos wlyb dros ben!
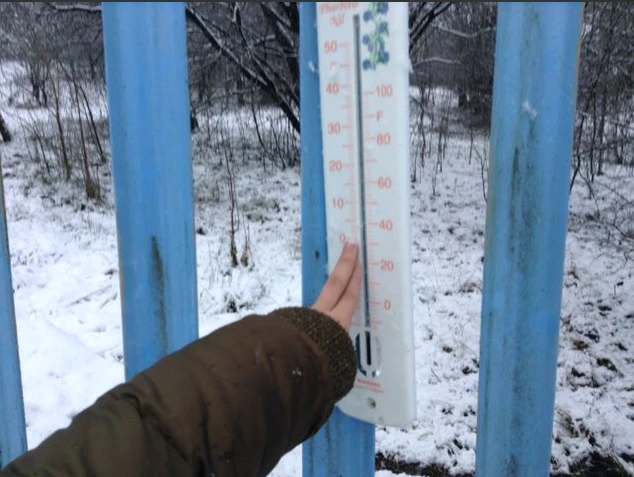
Ysgol Carreg Emlyn: Roedd yr ysgol ar gau Dydd Llun a Dydd Mawrth oherwydd yr eira.
Pembroke Primary School: We have planted tulips in pots also in school and it will be interesting to see how they compare to the daffodils and crocus. Professor Plant: That will be interesting, let me know how they compare Bulb Buddies!
Portpatrick Primary School: Shoots are stretching out of the ground :) . Professor Plant: What a lovely way of describing the sprouting of plants Bulb Buddies!
Inverkip Primary School: We really enjoyed doing it. We really want to do it again. Professor Plant: I’m glad to hear you are enjoying the project Bulb Buddies. Keep up the good work!
Newton Primary School: It's been a lovely week. It's been quite cold, but mainly dry. Four plants have started to grow over the weekend and by the end of the week they were around 2cm tall. Professor Plant: Gosh Bulb Buddies, thank you for keeping such a close eye on your plants. It will be interesting to see how much they grow week by week!
Darran Park Primary: There hasn't been any change to our bulbs this week.
Auchenlodment Primary School: We can see some roots growing out the bottom of the pots.
Ysgol San Sior: Our plants are growing well.
Darran Park Primary: We had a lot of snow on the weekend the temperature was very cold and below freezing on Monday and Tuesday. The temperature rose a little on Wednesday and it rained a lot.
Carnbroe Primary School: Hi Professor Plant last week we had snow,snow,snow! On Tuesday the rainfall cup was filled with snow because of the low temperature. On Friday we got sent home because of the red warning about a blizzard coming our way. Our bulbs look safe and are still sleeping. Professor Plant: Wow Bulb Buddies, it sounds as though you have had some extreme weather! Thank you for keeping me up dated.
St Julians Primary School: Melted snow increased our rainfall total on Monday. Our plants didn't seem to mind the colder weather!
Newton Primary School: A chilly week on the playground!
Beaufort Hill Primary School: Closed Monday and Tuesday due to snow.
St. Nicholas Primary School: We had a snow day on Monday - the 40mm (42mm) was ice in our rain gauge!
Hudson Road Primary School: It is getting colder and we have had heavy rain again
St Paul's CE Primary School: Frosty every morning, sunny spells.
Peterston super Ely Primary School: It was a wet week this week!
St Andrew's RC Primary School: We hope you have a merry Christmas and a happy new year. Professor Plant: Thank you Bulb Buddies, I hope you all enjoyed your holidays!
St Michael's CE (Aided) Primary School: There has been snow laying on our playground 11/12 December.
Canonbie Primary School: It's Christmas jumper day today so we were all wearing our Christmas jumpers as we were out measuring rainfall.