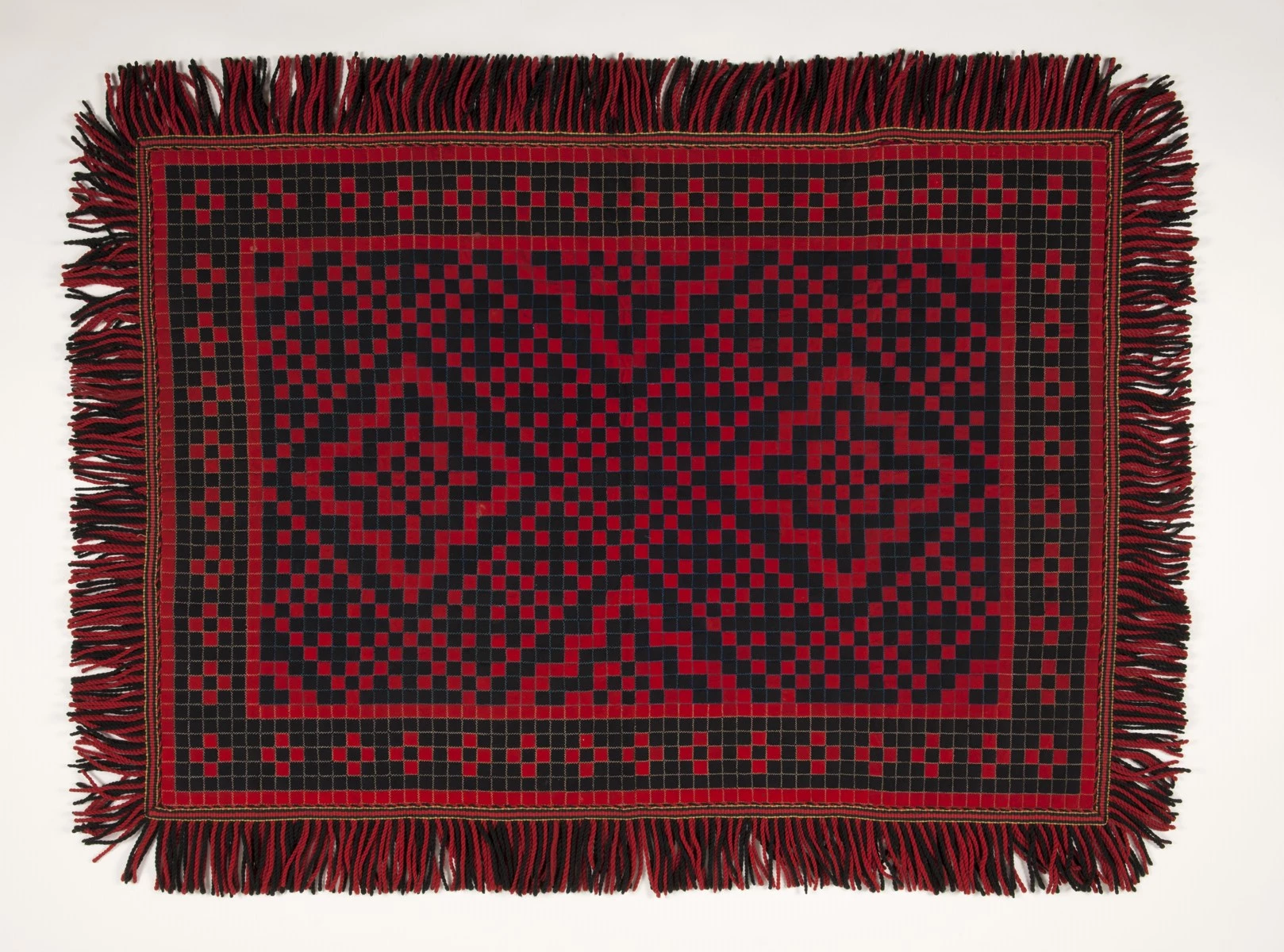
Amynedd y milwr - clytwaith Richard Evans, 1883
, 7 Medi 2016
Wrth wneud gwaith gyda’r Fforwm Ieuenctid, darganfyddais fod yna glytwaith i orchuddio cist o ddroriau (‘patchwork chest of drawers cover’) yng nghasgliad Sain Ffagan a gafodd ei greu gan fy hen hen ewythr, Richard Evans o Lanbrynmair, yn ystod ei amser yn gwasanaethu fel milwr yn India. Mae wedi ei greu o ddefnydd gwlanog trwchus coch a du ac felly tybiwyd ei fod wedi ei bwytho o ddillad milwr, ac yn ôl yr hyn sydd wedi ei arysgrifio ar ei gefn, roedd yn ‘Rhodd i fy Mam Sarah Evans 1883.’ Fe wnaeth y rhoddwr (Miss Ceridwen E Lloyd), sef nith i Richard Evans, ysgrifennu llythyr gyda’r gwrthrych a ymunodd â’r casgliad yn 1962, yn nodi “roedd ganddo fwy o amynedd na llawer ohonom heddiw.”
Roedd yr amynedd angenrheidiol i wneud gwniadwaith yn un o’r rhesymau pam ddaeth y grefft yn rhan o fywyd i rai mewn gwersylloedd milwrol. Yn ogystal â bod yn sgil ymarferol er mwyn gallu trwsio eu lifrau, roedd milwyr yn cael eu hannog i ddechrau gwnïo fel ffordd o ymlacio. Cefnogwyd y syniad gan fudiadau dirwest yn y bedwaredd ganrif ar bymtheg wrth iddynt weld gwnïo fel ffordd o gadw’r milwyr rhag demtasiynau yfed a gamblo, yn enwedig yng ngwres India. Roedd y grefft hefyd yn cael ei hybu fel rhan o therapi milwr mewn ysbyty er mwyn lleddfu diflastod. Mae yna enghraifft o waith tebyg yn y casgliad yn Sain Ffagan – gemwaith a gafodd ei greu gan y Corporal Walter Stinson pan roedd yn glaf yn Ysbyty VAD Sain Ffagan yn 1917-18.
Roedd gogwydd fwy emosiynol ar y math yma o waith hefyd. Weithiau, crewyd cwiltiau allan o lifrau cyd-filwyr a fu farw ar faes y gad i ddangos ffyddlondeb a gwladgarwch. Roedd gan y grefft bwrpas tu hwnt i’r cyfnod o ryfela hefyd, gan fod dysgu i wnïo yn gallu cael ei gysylltu ag ennill arian ar ôl gadael y fyddin. Yn y casgliad, mae yna ddarlun gwlân a oedd wedi ei brynu gan hen dad-cu y rhoddwr gan gyn-filwr oedd wedi colli ei goes wrth ymladd.
Mae llu o resymau felly i esbonio pam ddaeth gwniadwaith yn grefft fwy poblogaidd i filwyr. Daeth buddion y grefft i ddisgyblaeth a gwellhad milwyr â’r grefft oedd wedi ei hystyried yn un fenywaidd ar hyd y blynyddoedd yn rhan o hunaniaeth milwyr yn ystod y cyfnod hwn – ac ysbrydoli fy hen hen ewythr, yn bictiwr o wrywdod milwr gyda’i getyn a’i fwstash (trydydd o’r chwith yn y rhes gefn) i greu clytwaith fel anrheg i’w fam.